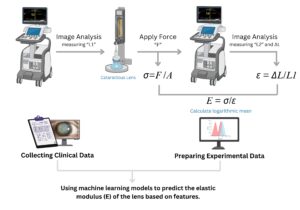
Lens stiffness is a key determinant in cataract surgery, especially during phacoemulsification, where ultrasound energy must be adjusted to lens hardness. Current methods rely on intraoperative judgment, limiting precision. This study introduces a non-invasive, data-driven approach to predict human lens stiffness preoperatively using supervised machine learning models trained on clinical and demographic features.
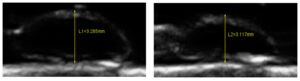
Fifty human lens nuclei were collected from extracapsular cataract extraction (ECCE) surgeries. Each lens was subjected to a controlled compressive load (0.2 N), and deformation was recorded using ultrasound imaging to calculate Young’s modulus as the ground-truth stiffness measure. Preoperative features included age, gender, cataract grade, lens diameter, diabetes status, and aspirin use—all routinely available in clinical settings.
Data preprocessing and model development were performed in Python using Scikit-learn. Multiple regression algorithms were trained and compared based on mean squared error (MSE) and R² scores to identify the most accurate and generalizable predictors.
Successful Prediction: The developed models accurately predicted human lens stiffness from preoperative, non-invasive data.
Best Models: Support Vector Regression (SVR) achieved the highest test accuracy (MSE = 0.0039, R² = 0.94), while Random Forest (RF) offered strong and balanced generalization (Train R² = 0.79, Test R² = 0.82).
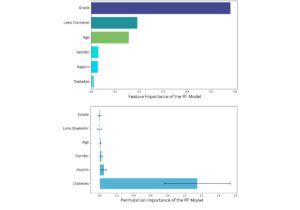
Feature Insights: Cataract grade, lens diameter, age, and diabetes status were the most influential predictors of stiffness.
Novel Comparisons: This study uniquely compared the relative impact of all features within a unified predictive framework—an analysis not previously performed in lens biomechanics.
Aspirin Effect: We also evaluated aspirin use as a predictive factor. Although its exact effect on cataract formation remains unclear, our model revealed measurable associations between aspirin intake and lens stiffness—providing new insight for future investigations.
Clinical Relevance: This non-invasive predictive approach may guide individualized surgical planning, optimize phacoemulsification energy, and enhance surgical safety and outcomes.
In Press, check back for updates.
