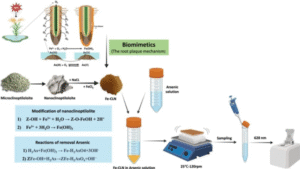
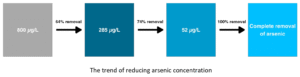
Access to clean drinking water remains a global challenge, particularly due to arsenic contamination in groundwater. Inspired by the iron plaque formation mechanism in rice roots, this project investigates a biomimetic approach to remove arsenic using iron-modified nanoclinoptilolite (Fe-nCLN). The iron modification enhances the surface properties of natural zeolite, increasing its adsorption efficiency for arsenic ions. Through surface characterization (DLS, XRD, BET, EDS, and zeta potential), the modified nanozeolite was optimized to mimic natural processes of arsenic immobilization, providing a cost-effective and sustainable solution for water purification in arsenic-affected regions.
To access the paper, Please Click Here.
