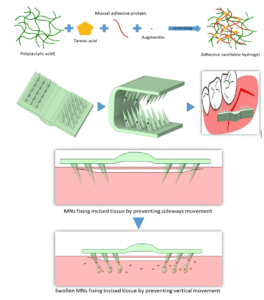
Periodontal surgeries typically conclude with the suturing of the gingival incision to facilitate wound closure and promote gingival tissue regeneration. Although suturing is considered the gold standard method, it presents significant operational and post-operational challenges. These include technical difficulties that extend operational time due to limited visibility and access, potential tissue trauma during the procedure, and post-operative complications such as infection risk, patient discomfort, inflammation, and swelling.
Inspired by the bidirectional orientation of Gila monster teeth, we developed an adhesive patch comprising a multidirectional hydrogel-forming microneedle (HFMN) array, which is loaded with augmentin antibacterial drug. This design facilitates Physical interlocking with gingival tissue. The interlocking mechanism is achieved through the swelling of the microneedle tips and the intricate design of the microneedles, which prevents both vertical and lateral detachment from the gingival tissue. This innovative design has the potential to replace sutures in periodontal surgeries, offering a more straightforward approach with a reduced risk of infection.
