
Professor of Stem Cell Engineering
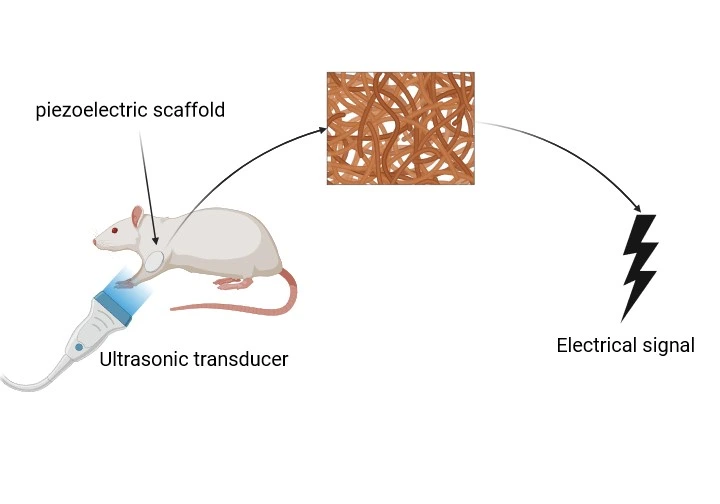
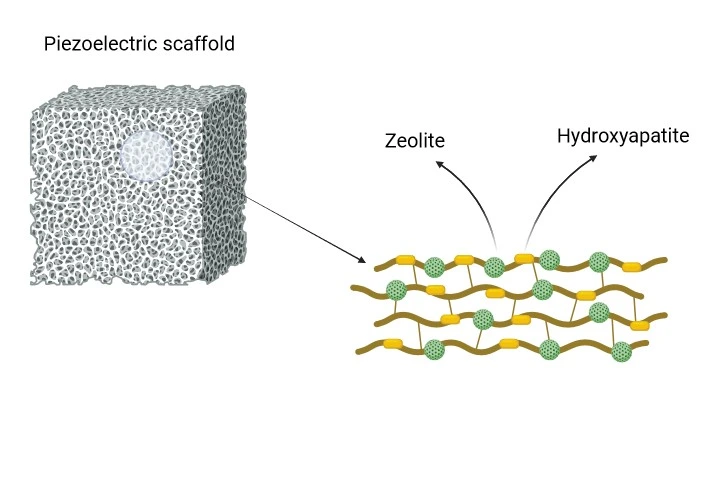
PiezoCart Composition and Characteristics
Scaffold: Zeolite / Hydroxyapatite (HA)
Drug/Growth Factor: None
Cells: Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells (hMSCs)
Key Features:
• Piezoelectric scaffold generates electrical signals under mechanical load
• Supports cell adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation
• Mimics natural electro-mechanical microenvironment of cartilage
• Biocompatible and osteo-conductive structure from HA
• Porous architecture for nutrient diffusion and waste removal
Mechanism of Action
Mechanical loading (e.g., walking) induces electrical polarization in the scaffold
Generated bioelectric signals stimulate hMSC chondrogenesis
Promotes extracellular matrix (ECM) synthesis, especially type II collagen and proteoglycans
Facilitates integration with native cartilage and subchondral bone
Conclusion
PiezoCart represents a next-generation cartilage scaffold that leverages mechanically induced electrical stimulation to enhance the chondrogenic potential of hMSCs. By combining the structural support of hydroxyapatite and the piezoelectric response of zeolite, this platform offers a promising drug-free and non-invasive strategy for treating cartilage defects, with strong potential for translation into clinical orthopedic therapies.
Have questions about our lab services or research capabilities?
Connect with our experts for tailored guidance and technical insight.